Have you heard of a condition known as Azoospermia? You will learn more about azoospermia in this article, its meaning, types, treatment, and drugs in Nigeria.
What is Azoospermia?
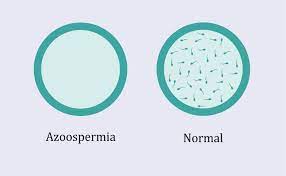
photo credit: andrologycenter
When a man’s ejaculate has no detectable sperm, it is said to have a condition known as azoospermia (semen). A condition known as azoospermia causes infertility in men.
Azoospermia is a condition in which a man’s ejaculate lacks sperm (No sperm count). Here’s a little knowledge on how the human body functions: The testicles are the organs responsible for the production of sperm. The seminal duct fluid is mixed with it as it passes through the reproductive system. Semen is the thick, white ejaculate that emerges from the penis when sperm and fluid combine.
In the case of azoospermia, Sperm is not present in your ejaculate. The word “low sperm count” may be known to you, but the term “azoospermia” means “no sperm count.”
Types of Azoospermia?
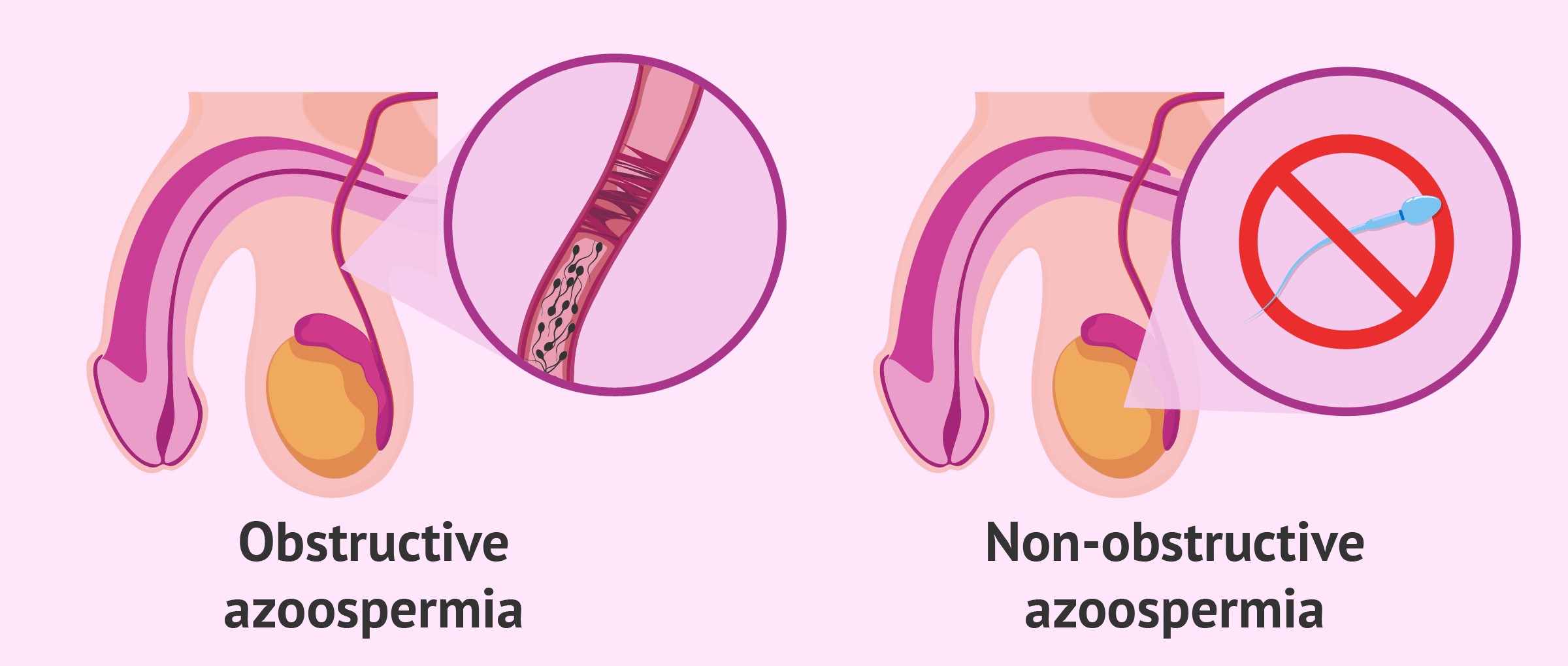
Photo credit: inviTRA
The three forms of azoospermia are as follows:
-
Pre-testicular azoospermia (non-obstructive)
This kind of azoospermia (non-obstructive) is characterized by an inability to produce sperm-creating hormones prior to ovulation.
2. Testicular azoospermia (non-obstructive)
Non-obstructive testicular azoospermia is brought on by problems with the testicles’ structure or function.
3. Post-testicular azoospermia (obstructive)
Obstructive post-testicular azoospermia is characterized by difficulties ejaculating as a result of a blockage in the reproductive canal.
Causes of Azoospermia
Azoospermia is caused by a variety of factors. Many things may cause azoospermia such as a blockage or infection in the male genitalia, damage to the male reproductive system as a result of surgery, or a person’s lifestyle choices such as taking too many medicines, and drinking too much alcohol, or abusing illicit drugs.
Azoospermia affects around 2% of the world’s male population. Oligospermia is a more common occurrence. The limited number of sperm cells in the testes is known as oligospermia ( low sperm count). It affects around 15% of all males and 40% of men undergoing infertility evaluations.
Signs and Symptoms of Azoospermia
You can have azoospermia without knowing until you have an issue i.e being unable to conceive. Other indications and symptoms, such as hormone imbalances or genetic chromosomal problems, may have a stronger connection to the underlying reasons.
Alternatively, you may have the following symptoms:
- a problem with sex life
- a sexually suggestive experience
- a reduction in a body or facial hair
- the testicles may be inflamed or swollen
Drugs for azoospermia in Nigeria
Obstructive and non-obstructive forms of azoospermia need different approaches to treatment. When azoospermia is not obstructed, fertility medications such as:
- follicle-stimulating steroid (FSH)
- Anastrazole
- hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) (HCG)
- Letrazole
- Bromocriptine
- Testerone Injections
- clomiphene (clomid)
What is the treatment for azoospermia?
Azoospermia treatment relies on the root cause. In many cases, azoospermia is diagnosed and treated with the use of genetic testing and counseling. Methods of treatment include:
Surgery may be necessary if azoospermia is caused by a blockage in the tubes or if malformed or never-developed tubes are to blame.
Hormone therapies may be necessary if decreased hormone production is the primary reason. An FSH, HCG, clomiphene, anastrozole, and letrozole are some of the hormones that may be used to stimulate the follicles.
If a varicocele is to blame for an inability to produce sperm, the troublesome veins may be surgically cut up, preserving the surrounding tissues.
With a thorough biopsy, some men are able to extract sperm straight from their testicles. In vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection may be performed if sperm are present in the testes, epididymis, or vas deferens (the injection of one sperm into one egg). As azoospermia may be passed on to future generations, your healthcare professional may propose genetic testing of your sperm before attempting assisted conception.
Any Infections
If there is a current infection, it should be addressed first before moving on to other options. Up to one-fourth of men have no symptoms of illness, even though they may show signs of infection (such as uncomfortable urinating). The infection may nevertheless have a detrimental impact on their fertility and cause long-term harm to the reproductive system even if there are no obvious symptoms.
Operative Reparation
With microsurgical therapy, certain instances of obstructive azoospermia may be treated by re-establishing blocked or damaged connections. Retrograde ejaculation and the removal or treatment of a varicocele may both be accomplished by surgical means.
When azoospermia is surgically corrected, it may be possible to conceive naturally. Surgery isn’t going to fix the issue immediately, however. An analysis of the patient’s semen will be requested three to six months after the operation has been completed.
It is possible for a couple to conceive naturally if sperm levels are normal and there are no reproductive issues in the female spouse. Other methods might be explored if sperm counts are still abnormal following surgery.
Medications or Hormone Replacement Therapy
Medication may be used to treat azoospermia in rare circumstances. Medications may be used to cure retrograde ejaculation, which in turn can lead to natural conception. Some men with azoospermia may benefit from hormone therapy to boost sperm production. Sperm cells may be able to return to semen with the help of hormones.
Natural therapies may be able to aid you
Azoospermia may or may not respond to home remedies for sperm production. While some medicines and dietary modifications may help raise a low sperm count, they may have little effect on sperm that is lacking because of a blockage or a hereditary problem (if at all).
The fact that you can assist yourself by eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, drinking enough water, and managing your stress isn’t a disclaimer. Whether you have a medical condition, you may want to see your doctor see if any natural therapies will assist you.
Try these out:
- Make sure you’re getting enough nutrients by eating a diet rich in whole, natural foods that are high in protein.
- Regularly work out. By doing so, you may be able to increase
- Increased amounts of testosterone
- Reduce your stress levels by practicing yoga or meditation. Cortisol (the stress hormone) may have an effect on a person’s health
- production of testosterone
- Find out whether there are any herbal or dietary supplements, such as Tribulus Terrestris, that may help boost male fertility.
- Black seed, Coenzyme Q10, folic acid, horse chestnut, L-carnitine, Panax ginseng, and zinc are just a few of the supplements available.